Tổng số bài đăng 389.
In a significant stride towards sustainable energy and environmental conservation, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is gearing up to implement comprehensive strategies for the reuse of electric vehicle (EV) batteries. This initiative, detailed in a recent report by the Economic Research Institute for ASEAN and East Asia (ERIA), underscores the region’s commitment to tackling local air pollution, enhancing energy security, and mitigating climate change.
The Growing Importance of EVs in ASEAN
Electric vehicles are increasingly seen as a crucial component in the fight against air pollution and climate change. Countries like Indonesia and Thailand are leading the charge, with ambitious plans to develop robust EV manufacturing industries. Indonesia, for instance, aims to phase out internal combustion engine vehicles by 2040 and is investing heavily in developing a domestic battery manufacturing sector. Thailand, on the other hand, aspires to become the regional hub for EV production.
However, the rapid adoption of EVs brings with it the challenge of managing the lifecycle of EV batteries. As the number of EVs on the road increases, so too will the volume of used batteries. By 2040, it is projected that ASEAN will generate between 325 gigawatt hours (GWh) and 2,166 GWh of used EV batteries, depending on the rate of EV adoption.
Learning from Global Practices
The ERIA report draws on global best practices to provide a roadmap for ASEAN countries. It examines the regulatory frameworks and initiatives in Europe, the United States, Japan, and China, offering valuable insights into how these regions manage EV battery reuse and recycling.
In Europe, the focus is on creating a circular economy with stringent regulations that ensure transparency and environmental performance throughout the battery lifecycle. The European Union’s revised Batteries Directive mandates carbon footprint declarations and the use of recycled materials, setting a high bar for sustainability.
The United States, while lacking federal regulations, has seen significant state-level initiatives, particularly in California. The state has established advisory groups to develop policies aimed at maximizing the reuse and recycling of lithium-ion batteries.
Japan’s approach is characterized by strong industry collaboration and government support. The Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association has launched a joint collection network, and the government has issued guidelines for battery performance evaluation, ensuring that reused batteries meet high safety and quality standards.
China, with its rapid EV market growth, has implemented a comprehensive traceability system for EV batteries. This system tracks batteries from production to disposal, ensuring that they are reused or recycled efficiently.
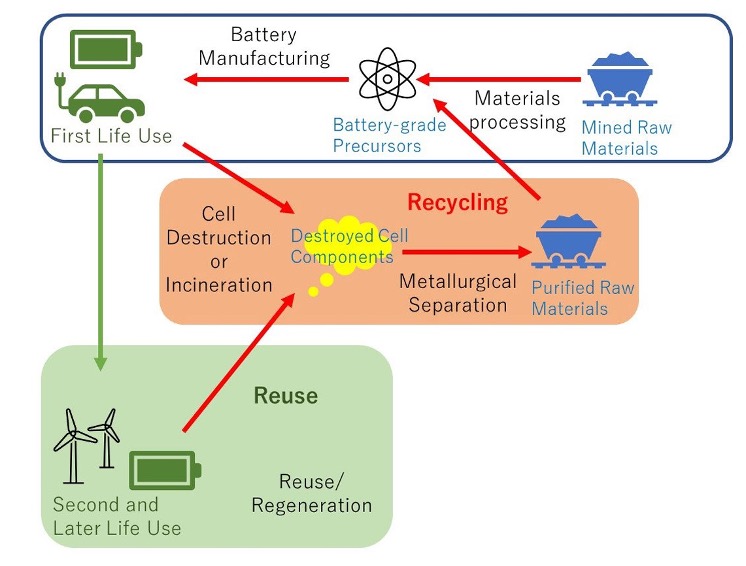
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Reusing EV batteries is not only environmentally beneficial but also economically viable. The cost of new EV batteries has dropped significantly, from $1,100 per kilowatt hour (kWh) in 2010 to $137 per kWh in 2020. This trend is expected to continue, making reused batteries a cost-effective option for various applications.
The environmental benefits are equally compelling. Reusing EV batteries can lead to substantial energy savings, reduce the need for new raw materials, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, using repurposed batteries for residential energy storage or as backup power for renewable energy sources can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of these systems.
Policy Recommendations for ASEAN
To realize the full potential of EV battery reuse, the ERIA report outlines several key recommendations for ASEAN policymakers:
1. Health and Safety: Establish monitoring mechanisms to ensure the safety of reused batteries.
2. Technology and R&D: Invest in research and development to improve battery performance evaluation and repurposing processes.
3. Regulatory Framework: Develop clear regulations to govern the reuse and recycling of EV batteries.
4. Economic Incentives: Provide incentives to lower the costs of repurposing batteries.
5. Collection Systems: Create coordinated systems involving manufacturers, retailers, and recycling entities to manage battery collection and reuse.
ASEAN’s proactive approach to reusing EV batteries represents a significant step towards sustainable energy and environmental stewardship. By learning from global best practices and implementing robust policies, the region can effectively manage the lifecycle of EV batteries, ensuring that the benefits of electric vehicles extend far beyond their initial use. This initiative not only supports ASEAN’s environmental goals but also positions the region as a leader in sustainable energy practices.









