Total number of posts 30.
According to ASEAN Economic Integration Brief 2024 (Issue 15, July 2024), ASEAN economies are projected to experience slight growth, reaching 4.6% in 2024 and rising to 4.7% in 2025. This outlook is set against a backdrop of strong global economic recovery post-COVID, reflecting resilience againts financial challenges. Growth is expected to be primarily driven by increased tourism and the recovery of the global semiconductor and electronics industries. Trade performance in 2024 is also expected to show promising signals and optimistic prospects across most markets. Additionally, easing inflation pressures and stable borrowing costs are anticipated to create a more favorable financial environment, further supporting economic activities in the region.
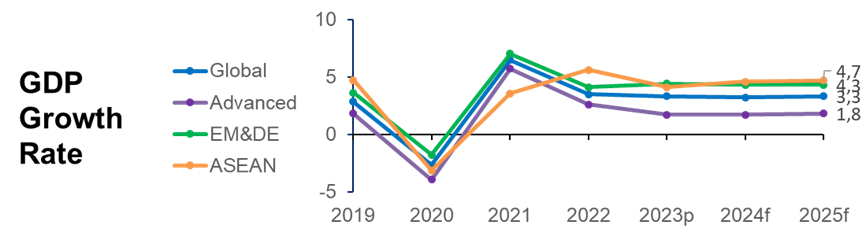
Source: asean.org
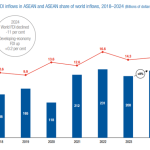
Intra-ASEAN trade saw negative growth in 2023 due to multiple factors. Conflicts in the Middle East disrupted trade routes via the Red Sea, doubling shipping costs and impacting supply chains. Additionally, China’s economic slowdown, as China is ASEAN’s largest trading partner, contributed to the decline in trade. Among ASEAN's top three export commodities, two saw significant drops in the second half of 2023 compared to the same period in 2022: electronics (HS-85) decreased by 4%, and mineral fuels (HS-27) decreased by 17%. Machinery (HS-84) remained stable with a slight increase of 0.3%.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) into ASEAN continued to show regional resilience, with a modest increase of 0.3% from 2022 to 2023, according to preliminary data from ASEANstats. Although economic uncertainty and geopolitical risks led some companies to delay new investments, overall growth remained positive. This growth was mainly due to large investments from the United States in finance and insurance, reaching USD 74.4 billion, up 32.4% from 2022. The three consecutive years of FDI growth in ASEAN have reinforced its appeal to foreign investors.
Inflation pressures in ASEAN continue to ease thanks to declining global commodity and product prices and the gradual stabilization of supply chains post-pandemic. ASEAN’s inflation rate is projected to decrease from 4.1% in 2023 to 3.2% in 2024 and 3.0% in 2025, gradually returning to pre-pandemic averages. Although food inflation is also subsiding, rice prices remain high due to weather phenomena like El Niño, La Niña, and export restrictions from India affecting costs.

Forecasted risks impacting ASEAN’s economic outlook include escalating geopolitical tensions and conflicts, such as those disrupting trade routes via the Red Sea, which could cause supply chain disruptions, drive up commodity prices, and increase economic instability—particularly affecting trade-dependent economies like ASEAN. The region is also vulnerable to changes in global monetary policies, as prolonged high-interest rates could lead to capital outflows, currency depreciation, higher inflation, and growth limitations. Global economic “fragmentation” may also have ripple effects, reducing demand for ASEAN exports and impacting overall economic activity. Risks related to weather, climate change, and phenomena like El Niño and La Niña could disrupt agricultural production, raise food prices, and pose food security risks, particularly in Myanmar, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Economic development priorities for ASEAN
Although ASEAN’s economic outlook remains positive, the region still faces major challenges requiring close coordination among member states and appropriate national strategies. To respond to the complex economic landscape and ensure sustainable growth, ASEAN should prioritize enhancing regional cooperation to address shared challenges such as supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and climate change impacts. Diversifying trade and investment partners is essential to reduce dependence on certain major partners and sectors, boost intra-ASEAN trade, and explore opportunities in emerging markets and high-growth industries. Accelerating digital transformation through investment in digital infrastructure and enterprise skill development will enhance competitiveness and innovation capacity. Finally, promoting sustainable, inclusive, and environmentally responsible growth will ensure long-term prosperity for the ASEAN region and its people.