Total number of posts 468.
Amid global challenges like climate change and resource depletion, the circular economy (CE) has become an inevitable trend for nations worldwide, aiming for sustainable and inclusive development.
The traditional economy, or linear economy, operates on a "take, make, use, dispose" model, relying heavily on natural resources and often leading to significant waste when products are not recycled or reused. This approach exacerbates resource depletion and environmental pollution, undermining long-term sustainability. With rapid population growth and mounting pressures on natural resources, the limitations of the linear model have become increasingly evident, driving a shift toward more sustainable models such as circular economy.
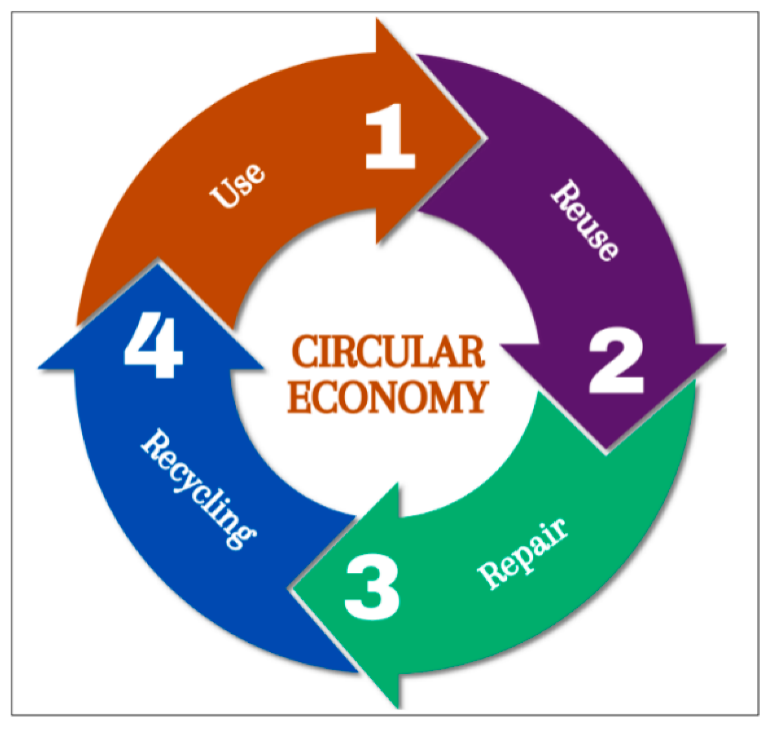
Circular economy is a sustainable economic model where products, materials, and resources are reused, recycled, and given extended lifespans instead of being discarded after a single use. Its goals include optimizing resource use, minimizing waste, and reducing environmental impacts. circular economy promotes environmentally friendly product designs, renewable resources, and technologies that convert waste into new production inputs. This model not only conserves natural resources but also fosters sustainable economic value, helping businesses and nations achieve green growth and carbon reduction targets.
Globally, circular economy has gained momentum as governments and the private sector recognize the impact of climate change. Leading the way, the European Union has implemented circular economy strategies to cut waste and meet carbon emission goals. In Vietnam, the government prioritizes CE in its national socio-economic development strategy, encouraging recycling, resource efficiency, and regional collaboration within ASEAN for a green and sustainable economy.
Recognizing global challenges and the necessity of economic transformation, ASEAN is also advancing circular economy to achieve sustainable and inclusive growth. ASEAN is building a supportive ecosystem for CE, emphasizing standard harmonization, green trade facilitation, supply chain greening through technology, and increased financing for green projects. Incentives such as tax breaks, financial aid, and regulatory support for circular products are crucial to boosting both supply and demand.
In 2021, ASEAN established the ASEAN Circular Economy Framework, outlining a long-term vision, priority sectors for action, and inter-sectoral cooperation mechanisms to expedite circular economy adoption in the region. The framework aims to strengthen ASEAN's resilience, improve resource efficiency, and foster sustainable growth by aligning standards, enhancing regional supply chain connectivity, promoting innovation and digitization, and encouraging sustainable financing and efficient resource use.

While adopting circular economy is a long-term journey for ASEAN, particularly given varying development levels among its member states, prioritizing key sectors such as agriculture, energy, finance, and transportation will accelerate progress. Additionally, enhancing environmental transparency among businesses is essential for fostering accountability and sustainable practices across the region.
The circular economy is not only a solution to global challenges but also an opportunity for nations, particularly the ASEAN region, to build a resilient, sustainable, and inclusive economy. The transition from a linear to a circular economy requires strong commitment from governments, businesses, and society as a whole, along with close collaboration among countries in the region. With a clear roadmap and appropriate supporting policies, ASEAN has the potential to become a pioneering model in circular economic development, contributing not only to green economic growth but also to ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.














